Review
, Volume: 16( 15)An Updated Review on Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography
- *Correspondence:
- Chandraman K , Department of Pharmaceutics, Bharat Technology, Uluberia, Howrah, India, Tel: +91-7797923218; E-mail: sirwal0711@gmail.com
Received: July 01, 2016; Accepted: August 27, 2016; Published: August 31, 2016
Citation: Chandraman K. An Updated Review on Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography. Anal Chem Ind J. 2016;16(15):114.
Abstract
UPLC can be regarded as latest invention for liquid chromatography. UPLC refers to Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography. It brings drastic changes in sensitivity and speed of analysis. It has instrumentation that can be operated at higher pressure as compared to HPLC. This review includes the theories & principle of Chromatography along with the Comparison between HPLC & UPLC, advanced feature is listed here in this review. Some of the most recent applications of UPLC are also included here along with examples.
Keywords
UPLC; HPLC; Chromatography; Sensitivity; Time; Principle
Introduction
Chromatography is a non-destructive procedure for separating a mixture of components in to individual components with the help of a porous medium under the influence of solvents. Before 2004, HPLC was the most frequently used technique for separating a mixture of components into individual components. But due to some limitation a new technique has been introduced by the scientist which is highly efficient and advanced and also overcome some of the limitation of HPLC and the technique popularly known as "Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography (UPLC)" [1-5].
UPLC is regarded as new invention for liquid chromatography. UPLC brings drastic changes in sensitivity, resolution and speed of analysis can be calculated. It has instrumentation that can perform at higher pressure as compared to that used in HPLC & in this system uses fine particles (less than 2.5 μm) and mobile phases at maximum linear velocities reduces the length of column also reduces solvent consumption and saves time. This review introduces working principle of UPLC along with some of the most recent work in the field. According to the van Deemter equation, as the size of particles reduces to below 2.5 μm, there is a significant gain in efficiency. Therefore, by using smaller particles, speed and peak capacity can be extended to new limits, of liquid chromatography [6-10].
Brief History
Chromatography is a new technique which was first invented by Tswett, a Russian Botanist in 1906 in Warsaw. In that year, he successfully done the separation of chlorophyll, xanthophylls and several others coloured substances by percolating vegetable extracts with the help of column of calcium carbonate. The column of calcium carbonate act as an adsorbent and the different substances get adsorbed to different extent and this gives rise to coloured bands at different position, on the column. Tswett termed this system of coloured bands as chromatogram and the technique use as chromatography after the Greek words chroma and graphos meaning colour and writing respectively [11-17].
Considerable advances have since been made and the methods is used to separate coloured along with colourless substances. The column of calcium carbonate used in Tsweet method remains stationary and is therefore named as the stationary phase. The solution of vegetable extracts moves or flows down the column and is therefore termed as mobile phase. chromatography may be regarded as a technique of separation in which separation of solutes occurs between a stationary phase and a mobile phase [18-25].
In 1930 chromatography in the form of thin layer chromatography along with ion exchange chromatography was introduced as a separation technique. In 1941, Martin and synge introduced paper chromatography and latter gas chromatography in 1952. Apart from its use in analysis it is becoming a potential technique as a method for the preparation of very pure compounds in the fields like pharmaceutical industry or in the manufacture of pure chemicals. The recent spectacular developments in the field of bioscience are entirely because of the chromatographic methods of separation of bio-molecules.
Later on, the others techniques like HPLC was introduced which has been used in Many laboratories for a long period of time then after a new technique has been introduce recently called UPLC (Ultra performance liquid chromatography).
Principle
The principle for the separation can either be adsorption or partition. Hence they can be called as adsorption chromatography or partition chromatography.
Adsorption chromatography
When adsorbate or mixture compounds is dissolved in mobile phase (eluent) travels through a column of stationary phase (adsorbent), they move according to the relative affinities towards stationary phase.
The compound which has more affinity for stationary phase travels slower and that having low affinity towards stationary phase travels faster. Hence the compounds are separated. No two compounds have the same affinity for a combination of stationary phase, mobile phase and other conditions.
Partition chromatography
The most widely used type of UPLC is partition chromatography. In the past, most of the applications have been to nonionic and polar compound of low moderate molecular mass (usually <3000.) The early forms of Partition chromatography liquid-liquid columns. These have been replaced in modern LC systems by liquid – bonded phase columns. In liquid – liquid chromatography, the liquid was held in place by physical adsorption. In bonded – phase chromatography, on the other hand, its attached by Chemical Bonding, resulting highly stable pickings insoluble in the mobile phase. Bonded Phase columns also compatible with gradient elution techniques. Therefore, our discussion focuses exclusively on bonded – phase partition Chromatography [26-35].
Instrumentation
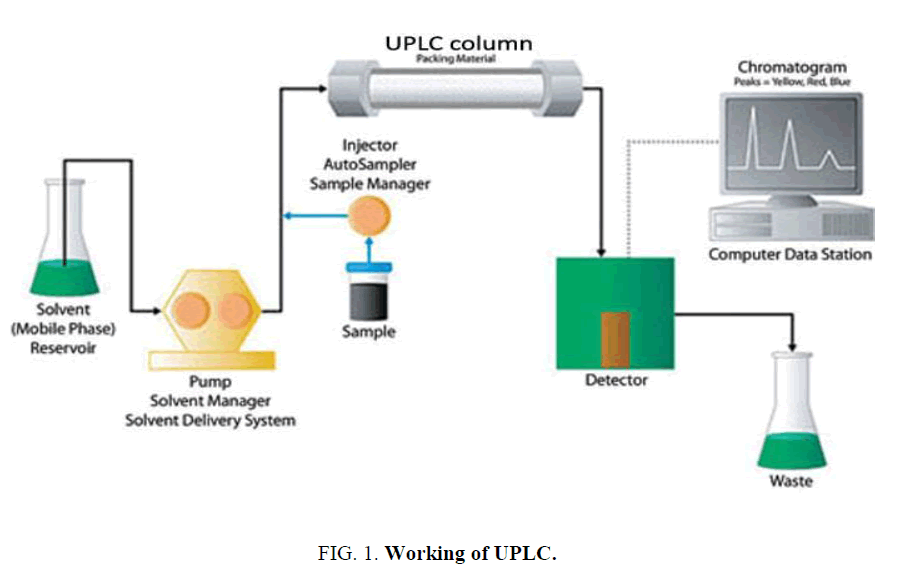
The various instruments used in the Ultra performance liquid chromatography are as follows (( Figure 1)).
• Sample injection
• UPLC columns
• Column manger & heater or cooler
• Detectors
Advantages
• It decreases the run time and increases sensitivity.
• Provides the sensitivity, selectivity, and dynamic range of LC analysis.
• Maintains the resolution performance.
• Expands scope of Multiresidue Methods.
• Faster analysis is possible with the use of a novel separation material which are of very fine particle size [42-44].
• The cost of operation in less.
• Solvent consumption is less.
• It decreases process cycle times, which helps to produce more product with limited resources too.
• Increases sample throughput and helps the manufacturers to produce more material that consistently meet and exceeds the product specifications, also potentially eliminate variability, failed batches, or the need to re-work material [45-53].
Disadvantages
• Due to increased pressure frequent maintenance is required and reduces the life of the columns of this type.
• In addition, the phases of below than 2 μm are generally non-regenerable and thus have limited use [54-58].
Application
Analysis of natural products and traditional herbal medicine
These technique is popularly use for the separation of natural products and traditional herbal medicine. It has a highly advanced detection and separation capabilities to identify active compounds that are presents in the samples of natural products and herbal medicine medicines.
Study of metabonomics /metabolomic
Metabonomics studies are carried out in labs to accelerate the development of new medicines. It provides a quick and robust method for detecting the changes, improves understanding of potential toxicity, and allows observing the capacity. The correct application of metabolomics and metabolomic information helps in the discovery, development, and manufacturing processes in the biotechnology and chemical industry companies
Identification of metabolite
Biotransformation of new chemical entities (NCE) is necessary for drug discovery. When a compound reaches the development stage, its identification becomes a regulated process. UPLC addresses the complex analytical requirements of new discovery by providing unmatched resolution, sensitivity, and mass accuracy [59-63].
ADME (Absorption, Distribution, Metabolism, Excreation) Screening:
Pharmacokinetics studies include studies of ADME. It studies important physical and biochemical properties like absorption, distribution, metabolism, elimination, etc. where such compounds show its activity against the target disease.
Manufacturing / QA / QC
Identification of purity, quality, safety and efficacy are the most important factors that need to be considered while manufacturing a drug product. For the successful production of quality pharmaceutical products, the raw materials need to meet the purity speciation. These can be achieved with the help of UPLC technique [64-68].
Impurity profiling
These techniques easily detect the impurities present if it is presents in very trace levels too. UPLC combines with same mass LC/MS, which by running with different low and high collision energies, has been successfully used for the detection of drug and endogenous metabolites.
UPLC fingerprint
It can be used for the identification of Magnolia officinalis cortex [69-75].
Conclusion
UPLC increases and expands the significance of chromatography. The main asset is a decrease of analysis time, which also reduces consumption of solvent which plays a vital role in analytical laboratory. It gives sharp and narrow peaks all categories of pharmaceutical drugs. It also facilitates the analysis of complex mixtures in relatively short time and the peaks obtained with the help of these method provides more information which is more convenient and clear that of HPLC. This technology thus creates a new opportunity for business profitability in highly efficient manner and helps the product to introduced in the within short period of time. Overall, it seems that UPLC can offer significant improvements in speed, resolution and sensitivity compared with conventional HPLC technique [76-79].
References
- Ashok K, Gautam S, Anroop N, et al. UPLC A Preeminent Technique in Pharmaceutical Analysis. ActaPoloniaePharmaceutica. 2012;69(3):376-7.
- Vandana P. Ultra-performance liquid chromatography: a review. IntRes JPharma. 2011;2(6):39-44.
- Reddy SKT, Balammal G, Kumar SA.Ultra-performance liquid chromatography: an introduction and review.IntJPharmaResAnal. 2012;2(1):24-31.
- Fingerhut R, Röschinger W, Markus H. A Rapid and Sensitive UPLC-MS/MS-Method for the Separation and Quantification of Branched-Chain Amino Acids from Dried Blood Samples of Patients with Maple Syrup Urine Disease (MSUD).IntJNeonatal Screen. 2016,2(2):2.
- Yuanbin Li, Sheng N, Wang L, et al.Analysis of 2-(2-Phenylethyl) chromones by UPLC-ESI-QTOF-MS and Multivariate Statistical Methods in Wild and Cultivated Agarwood.Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(5):771.
- Montero O, Velasco M, Sanz-Arranz A, et al. Effect of Different Broad Waveband Lights on Membrane Lipids of a Cyanobacterium, Synechococcussp, as determined by UPLC-QToF-MS and Vibrational Spectroscopy.Biology. 2016;5(2):22.
- Zhan C, Xiong A, Shen D, et al. Characterization of the Principal Constituents of Danning Tablets, a Chinese Formula Consisting of Seven Herbs, by an UPLC-DAD-MS/MS Approach. Molecules. 2016;21(5):631.
- Boelaert J, Schepers E, Glorieux G, et al. Determination of Asymmetric and Symmetric methylarginine in Serum from Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease: UPLC-MS/MS versus ELISA.Toxins. 2016;8(5):149.
- Jae Won L, Mok HJ, Dae-Young L, et al. UPLC-MS/MS-Based Profiling of Eicosanoids in RAW264.7 Cells Treated with Lipopolysaccharide.Int J Mol Sci. 2016;17(4):508.
- Yang NA, Xiong A, Wang R, et al.Quality Evaluation of Traditional Chinese Medicine Compounds in XiaoyanLidan Tablets: Fingerprint and Quantitative Analysis Using UPLC-MS.Molecules. 2016;21(2):83.
- Song Y, Guo Y, Zhang X. Synthesis of Isotopically Labeled 13C3-Simazine and Development of a Simultaneous UPLC-MS/MS Method for the Analysis of Simazine in Soil.Molecules. 2016;21(1):89.
- Zou D, Wang J, Zhang B, et al. Analysis of Chemical Constituents in Wuzi-Yanzong-Wan by UPLC-ESI-LTQ-Orbitrap-MS.Molecules. 2015;20(12):21373-404.
- Jae Won L, Seung-Heon J, Geum-Soog K, et al. Global Profiling of Various Metabolites in Platycodon grandiflorum by UPLC-QTOF/MS. Int J Mol Sci. 2015;16(11):26786-96.
- MuratovicZA, Hagström T, Rosén J, et al. Quantitative Analysis of Staphylococcal Enterotoxins A and B in Food Matrices Using Ultra High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS).Toxins. 2015;7(9):3637-56.
- Wu ZF, Ya-Qi W, Wan N, et al. Structural Stabilities and Transformation Mechanism of Rhynchophylline and Isorhynchophylline by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography/Time-of-Flight Mass Spectrometry (UPLC/Q-TOF-MS). Molecules. 2015;20(8):14849-59.
- Lin Y, Xu W, Huang M, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Phenolic Acids, Flavonoids and Iridoid Glycosides in YinhuaKanggan tablet by UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS. Molecules. 2015;20(7):12209-28.
- Vlamis A, Katikou P, Rodriguez I, et al. First Detection of Tetrodotoxin in Greek Shellfish by UPLC-MS/MS Potentially Linked to the Presence of the Dinoflagellate Prorocentrum minimum. Toxins. 2015;7(5):1779-1807.
- Yan-Kang H, You-Yuan Y, Ya-Ning C. Characterization of Anthocyanins in Perillafrutescens var. acuta Extract by Advanced UPLC-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn Method and their Anticancer Bioactivity. Characterization of Anthocyanins in Perillafrutescens var. acuta Extract by Advanced UPLC-ESI-IT-TOF-MSn Method and Their Anticancer Bioactivity. Molecules. 2015;20(5):9155-69.
- Juin C, Bonnet A, Nicolau E, et al. UPLC-MSE Profiling of Phytoplankton Metabolites: Application to the Identification of Pigments and Structural Analysis of Metabolites in Porphyridium purpureum. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(4):2541-58.
- Shi-Yong G, Yun-Fei G, Qiu-Jia S, et al. Screening Antitumor Bioactive Fraction from Sauromatumgiganteum (Engl.) Cusimano&Hett and Sensitive Cell Lines with the Serum Pharmacology Method and Identification by UPLC-TOF-MS.Molecules. 2015;20(3):4290-306.
- Yan L, Yin P, Ma C, et al. Method Development and Validation for Pharmacokinetic and Tissue Distributions of Ellagic Acid Using Ultrahigh Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry (UPLC-MS/MS). Molecules. 2014;19(11):18923-35.
- Cui S, Li H, Wang S, et al. Ultrasensitive UPLC-MS-MS Method for the Quantitation of Etheno-DNA Adducts in Human Urine. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2014:1(10):10902-14.
- Lee J, Jung Y, Jeoung-Hwa S, et al. Secondary Metabolite Profiling of Curcuma Species Grown at Different Locations Using GC/TOF and UPLC/Q-TOF MS. Molecules. 2014:19(7):9535-51.
- Błaszczak-Świątkiewicz K, Correia Almeida D, De Jesus Perry M, at el. Synthesis, Anticancer Activity and UPLC Analysis of the Stability of Some New Benzimidazole-4,7-dione Derivatives. Molecules. 2014;19(1):400-13.
- Li-Wen C, Mei-Ling H, Tung-Hu T. Pharmacokinetics of Dibutyl Phthalate (DBP) in the Rat Determined by UPLC-MS/MS. Int J Mol Sci. 2013:14(1):836-49.
- Cu P, Han H, Wang R, et al. Identification and Determination of Aconitum Alkaloids in Aconitum Herbs and Xiaohuoluo Pill Using UPLC-ESI-MS. Molecules. 2012;17(9):10242-57.
- Yan-Hong S, Zhi-Yong X, Wang R, et al. Quantitative and Chemical Fingerprint Analysis for the Quality Evaluation of Isatisindigotica based on Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography with Photodiode Array Detector Combined with Chemometric Methods. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(7):9035-50.
- Salazar C, Jenny MA, Shulaev V. An UPLC-ESI-MS/MS Assay Using 6-Aminoquinolyl-N-Hydroxysuccinimidyl Carbamate Derivatization for Targeted Amino Acid Analysis: Application to Screening of Arabidopsis thaliana Mutants. Metabolites. 2012;2(3):398-428.
- Zhou W, Shu-Lan S, Jin-Ao D, et al. Characterization of the Active Constituents in Shixiao San Using Bioactivity Evaluation Followed by UPLC-QTOF and Markerlynx Analysis. Molecules. 2010;15(9):621730.
- Li K, Anne MS, Chung-Davidson YW, et al. Quantification of Oxidized and Unsaturated Bile Alcohols in Sea Lamprey Tissues by Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2016;21(9):1119.
- Gao M, Yang J, Wang Z, et al. Imultaneous Determination of Purpurin, Munjistin and Mollugin in Rat Plasma by Ultra High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry: Application to a Pharmacokinetic Study after Oral Administration of Rubiacordifolia L. Extract. Molecules. 2016;21(6):717.
- Lin L, He S, Ding L, et al. Efficient Preparation of Streptochlorin from Marine Streptomyces sp. SYYLWHS-1-4 by Combination of Response Surface Methodology and High-Speed Counter-Current Chromatography. Molecules. 2016;21(6):693.
- Cody JP, Ronner L, Rodgers L, et al. Quantification of Temozolomide in Nonhuman Primate Fluids by Isocratic Ultra-High Performance Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry to Study Brain Tissue Penetration Following Intranasal or Intravenous Delivery. Separations. 2016;3(1):4.
- Teng-Hua W, Zhang J, Xiao-Hui Q, et al. Application of Ultra-High-Performance Liquid Chromatography Coupled with LTQ-Orbitrap Mass Spectrometry for the Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of Polygonummultiflorum Thumb. and its Processed Products. Molecules. 2016:21(1):40.
- Amir A, Laakso I, Seppänen-Laakso T, et al. Analysis of Indole Alkaloids from Rhazyastricta Hairy Roots by Ultra-Performance Liquid Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. Molecules. 2015;20(12):22621-34.
- Chen D, Lin S, Xu W, et al. Qualitative and Quantitative Analysis of the Major Constituents in ShexiangTongxin Dropping Pill by HPLC-Q-TOF-MS/MS and UPLC-QqQ-MS/MS. Molecules. 2015;20(10):18597-619.
- Li G, Tang Z, Yang J, et al. Simultaneous Determination of Five Components in Rat Plasma by UPLC–MS/MS and Its Application to a Comparative Pharmacokinetic Study in BaiheZhimu Tang and Zhimu Extract. Molecules. 2015;20(4):6700-14.
- Lei F, Gao D, ZhangX, et al. In Vivo Metabolism Study of Xiamenmycin A in Mouse Plasma by UPLC-QTOF-MS and LC-MS/MS. Mar Drugs. 2015;13(2):727-40.
- Kouloura E, Danika E, Kim S, et al. Rapid Identification of Coumarins from Micromelumfalcatum by UPLC-HRMS/MS and Targeted Isolation of Three New Derivatives. Molecules. 2014;19(9):15042-57.
- Zhao Y, Jia L, Yang H, et al. Influence of Nonpolar Substances on the Extraction Efficiency of Six Alkaloids in Zoagumhwan Investigated by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography and Photodiode Array Detection. Molecules. 2012;17(12):13844-55.
- MA A, Mostafa MM, Bashanaini MSA. Enhanced Removal of Some Cationic Dyes from Environmental Samples Using Sulphuric Acid Modified Pistachio Shells Derived Activated Carbon. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:329.
- Rathore AS, Sathiyanarayanan L, Mahadik KR. Determination of Major Polyphenolic Components in Euphoria longana Lam. by Validated High Performance Thin-Layer Chromatography Method and Direct Analysis in Real Time Mass Spectrometry. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:330.
- Ibrahim F, El-Enany N, Shalan S, et al. Micellar High Performance Liquid Chromatographic Method for Simultaneous Determination of Clonazepam and Paroxetine HCl in Pharmaceutical Preparations Using Monolithic Column. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:331.
- Rathore AS, Sathiyanarayanan L, Mahadik KR. Characteristic Fingerprint Analysis of Mallotusphilippinensis by Ultra Performance Liquid Chromatography Electrospray Ionization Mass Spectrometry. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:332.
- Moussa A. In Vitro Glycation of the Pathogenic Prion Protein. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:e134.
- Ambekar A. Application of a Validated Stability-Indicating HPTLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Paracetamol and Aceclofenac and their Impurities. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:324.
- Piteni AI, Kouskoura MG, Markopoulou CK. HILIC Chromatography – An Insight on the Retention Mechanism. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:326.
- Heena, Gaurav, Rani S, et al. Speciation of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) Ions via Fabric Phase Sorptive Extraction for their Quantification via HPLC with UV Detection. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:327.
- Patel BD, Chhalotiya UK, Patel DB. Quantification of Newer Anti-Cancer Drug Clofarabine in their Bulk and Pharmaceutical Dosage Form. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:328.
- Alarfaj NA, El-Tohamy MF. A Novel Capillary Zone Electrophoresis Method for Simultaneous Separation and Determination of Nalbuphine Hydrochloride and its Related Antagonist Compounds. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:318.
- Bharti M, Yashila G. Lung Cancer and Nicotine. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:319.
- Mitroshkov A, Ryan JV, May-Lin T, et al. Comprehensive Isotopic and Elemental Analysis of a Multi-Oxide Glass ByMulticollector ICP-MS in Isotope Substitution Studies. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:320.
- Anumolu PD, Krishna VL, Rajesh CH, et al. Gas Chromatographic Assessment of Residual Solvents Present in Excipient-Benzyl Alcohol. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:321.
- Mishra PR, Satone D, Meshram DB. Development and Validation of HPLC Method for the Determination of Alcaftadine in Bulk Drug and its Ophthalmic Solution. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:312.
- Kuvshinova SA, Burmistrov VA, Novikov IV, et al. Selectivity, Thermodynamic and Anisotropic Properties of Substituted Liquid-Crystal Cyanoazoxybenzenes as Stationary Phases for Gas Chromatography. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:314.
- Kalsoom U, Bennett IJ, Boyce MC. A Review of Extraction and Analysis: Methods for Studying Osmoregulants in Plants. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:315.
- Rajamanickam V, Winkler M, Flotz P, et al. Comparison of Purification Strategies of Three Horseradish Peroxidase Isoenzymes Recombinantly Produced in Pichia pastoris. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2016;7:316.
- Trivedi MK, Branton A, Trivedi D, et al. Investigation of Isotopic Abundance Ratio of Biofield Treated Phenol Derivatives Using Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J Chromatograph SeparatTechniq. 2015;S6:003.
- Albert K, Gerhardt H, Lämmerhofer M. Investigating Insect Adhesion Secretions by Gas Chromatography-Mass Spectrometry. J Chromatograph SeparatTechniq. 2015;S6:001.
- Chauhan MK, Bhatt N. A Simple and Modified Method Development of Vancomycin Using High Performance Liquid Chromatography. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:296.
- Goswami J. Different Separation or Experimental Techniques for Clinical Chromatography: Small Review. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:297.
- Gineys M, Kirner T, Cohaut N, et al. Simultaneous Determination of Pharmaceutical and Pesticides Compounds by Reversed Phase High Pressure Liquid Chromatography. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:299.
- Mulubwa M, Rheeders M, Du Plessis L, et al. Development and Validation of High Performance Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) Method for Determination of Tenofovir in Small Volumes of Human Plasma. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:300.
- Mahmoud MA. Thermodynamics and Kinetics Studies of Mn (II) Removal from Aqueous Solution onto Powder Corn Cobs (PCC). J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:301.
- Ávila MC, Ponzi MI, Comelli NA. Hydration of α-Pinene over Heteropoly Acid H3PW12O40 and H3PMo12O40. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:302.
- Al Asmari AK, Ullah Z, Al Rawi AS, et al. Influence of Ionization and Sample Processing Techniques on Matrix Effect of a Pulmonary Artery Antihypertensive Drug. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:303.
- Bhatnagar P, Vyas D, Sinha SK, et al. Stability Indicating HPLC Method for Simultaneous Estimation of Entacapone, Levodopa and Carbidopa in Pharmaceutical Formulation. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:304.
- Cavalheiro J, Tessier E, Baltrons O, et al. Use of Polydimethylsiloxane Preconcentration Sorbent for the Analysis of Organotins in Water Samples. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:305.
- Zhang X, Shi L, Ding L, et al. Study on Quantitative Structure-Retention Relationships (QSRR) for Oxygen-Containing Organic Compounds Based on Gene Expression Programming (GEP). J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:306.
- Ali A, Uddin J, Ansari HN, et al. Electrospray Tandem Mass Spectrometric Study of a Furo-Furan Lactone in Heliotropiumeichwaldi. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:307.
- Guo WR, Ou SX, Long WP, et al. Simultaneous Detection Method for Mycotoxins and their Metabolites in Animal Urine by Using Impurity Adsorption Purification followed by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Detection. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:308.
- Gritti F. Retention Mechanism in Hydrophilic Interaction Liquid Chromatography New Insights Revealed From the Combination of Chromatographic and Molecular Dynamics Data. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:309.
- Karaś K, Kuczyńska J, Sienkiewicz-Jarosz H, et al. A Simple Bioanalytical Method for the Quantification of Levetiracetam in Human Plasma and Saliva. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:310.
- Gupta A, Sheth NR, Pandey S, et al. Determination of Quercetin a Biomarker in HepatoprotectivePolyherbal Formulation through High Performance Thin Layer Chromatography. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:285.
- Bokhart M, Lehner A, Johnson M, et al. Determination of Organochlorine Pesticides in Wildlife Liver and Serum Using Gas Chromatography Tandem Quadrupole Mass Spectrometry. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:286.
- Chen CT, Cheng CW, Hu YF, et al. Development and Validation of RP-UPLC Method for Determination of Related Substances in Risperdal®Consta®. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:287.
- Willmann L, Schlimpert M, Pan D, et al. Comprehensive Two-Dimensional Liquid Chromatography in Metabolome Analysis. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:288.
- Chen Z, Huang WX, Yu S, et al.Utilization of a Matrix Effect to Enhance the Sensitivity of Residual Solvents in Static Headspace Gas Chromatography. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:289.
- Feltens R, Roeder S, Otto W, et al. Evaluation of Population and Individual Variances of Urinary Phthalate Metabolites in terms of Epidemiological Studies. J Chromatogr Sep Tech. 2015;6:290.