Original Article
, Volume: 13( 2)Self-Functionalized, Oppositely Charged Chitosan-Alginate Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications
- *Correspondence:
- Pawar SH , Centre for Interdisciplinary Research D.Y. Patil University, Vidyanagar, Kasba Bawada, Kolhapur- 416006, Maharashtra, India, Tel: +91231 2601202; E-mail: ksneha.22@gmail.com
Received: July 14, 2016; Accepted: March 03, 2017; Published: March 06, 2017
Citation: Kumbhar SG, Pawar SH. Self-Functionalized, Oppositely Charged Chitosan-Alginate Scaffolds for Biomedical Applications.Biotechnol Ind J. 2017;13(2):130.
Abstract
Polymeric biomaterials have a significant influence in today’s health care technology. Polymers were the first experimentally designed biomaterials for human use. Chitosan and alginate are two natural and easily available polymers that are known to be biocompatible, biodegradable and retain good antimicrobial activity. When combined, they exhibit desirable characteristics and can be created into a scaffold for cell culture. Scaffolds based on chitosan and alginate offer advantages over other polymers due to their non-toxicity, biodegradability, biocompatibility, favorable mechanical properties, and are shown to be suitable for cell ingrowth and reconstruction. In this article the design, synthesis and properties of chitosan-alginate scaffolds, and their use as biomaterials in tissue engineering are reviewed.
Keywords
Chitosan; Alginate; Tissue engineering; Biomedical applications
Introduction
Tissue Engineering is addressed to create functional three-dimensional (3D) tissues combining scaffolds, cells and/or bioactive molecules [1]. It is an interdisciplinary discipline and involves basically three basic elements: scaffolds, cells and biomolecules [2].
A major goal in Tissue Engineering is the design of scaffolds capable of recreating the in vivo microenvironment that is provided mainly by the ECM. Thus, these structures should incorporate the appropriate biophysical, biomechanical and biochemical cues those guide cell proliferation, differentiation, maintenance and function [3]. The appropriate scaffold for tissue engineering will be one that is created with biology in mind. Ideally, the scaffold provides a temporary pathway for regeneration and will degrade while or after healing, thereby obviating the need to remove the material later and eliminating possible side effects allied with leaving materials in the body. Of course, attention must be paid to ensure the degradation products are non-cytotoxic [4].
Initially, scaffolds used for tissue engineering were derived from surgical materials; the tendency to adapt materials in current or prior use for other applications offers advantages from the perspective of regulatory agencies such as the Food and Drug Administration, but does not necessarily promote development of optimal materials with regard to performance characteristics needed for different tissues [5-7]. It is anticipated that the scaffolding biomaterial can be degraded as cells go through the process of forming their own supportive ECM; the permanent presence of implants almost always can be expected to elicit a foreign-body response. Material composition, surface chemistry, and topology influence the degradation [8].
Development of biomaterials also poses significant challenges. Formation of implanted tissue is greatly influenced by the composition, architecture, and Scaffold’s three-dimensional environment and biocompatibility of the biomaterial. In addition to being biocompatible, an ideal biomaterial scaffold for tissue regeneration can now be bioactive, biomimetic, biodegradable and bio responsive, providing signalling with spatio-temporal control and response which is selective to defined stimuli. Scaffold material’s mechanical strength needs to mimic the mechanical properties of the tissue it is intended to repair or replace. Moreover, material porosity, pore size distribution and continuity greatly influence the attachment of specific cell types and interaction of the biomaterials with the host [9].
Properties of Scaffolds
Scaffolds provide cells with a suitable growth environment, optimal oxygen levels, and effective nutrient and waste transportation as well as mechanical integrity. Scaffolds also provided 3D environments to bring cells in close proximity so that they can organize to form tissues. While the scaffold is being degraded, the cells produced their own extracellular matrix (ECM) molecules and eventually formed 3D structures mimicking the native tissue in morphology.
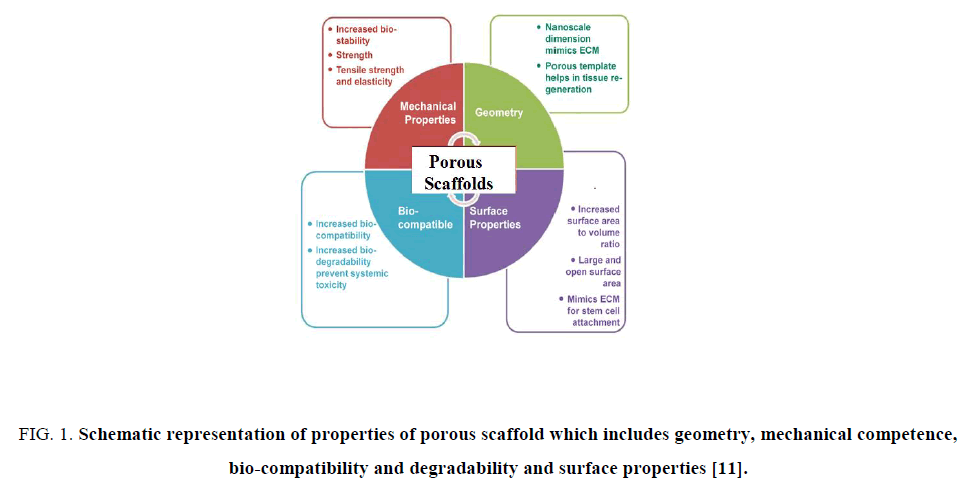
Many factors affect the selection and properties of scaffold. These include but not limit to biocompatibility, porosity, pore size, surface properties and pH, surface charge, biodegradability, mechanical properties, and ideally, the ability to recruit variety of cells. Several requirements have been identified as crucial for the production of scaffolds [10] some of them represented in Figure. 1.
Figure 1: Schematic representation of properties of porous scaffold which includes geometry, mechanical competence, bio-compatibility and degradability and surface properties [11].
1. The scaffolds should possess interconnecting pores of appropriate scale to favor tissue integration and vascularization.
2. They are made from material with controlled biodegradability or bio-resorbability so that tissue will eventually replace the scaffold.
3. They have appropriate surface chemistry to favor cellular attachment, differentiation and proliferation.
4. They possess adequate mechanical properties to match the intended site of implantation and handling.
5. They should not induce any adverse response.
6. They are easily fabricated into a variety of shapes and sizes.
The scaffold should possess acceptable biocompatibility and toxicity profiles. Biocompatibility is the ability of the scaffold to perform in a specific application without eliciting a harmful immune or inflammatory reaction. If the scaffold is nontoxic and degradable, new tissue will eventually replace it, whereas if it is nontoxic and biologically active, the scaffold will integrate with the surrounding tissue. However, Fibrous capsule may encapsulate the scaffold if it is biologically inactive. In the worst case rejection of the scaffold and localized death of the surrounding tissue can occur when the scaffold is toxic.
The scaffold material should be biodegradable and its degradation products should not be toxic and should be eliminated easily from the implantation site by the body, eliminating the need for further surgery to remove it. The scaffold’s degradation rate should be adjusted to match the rate of tissue regeneration so as to get disappeared completely once the tissue is repaired.
Biomaterials for Scaffold Fabrication
A number of biodegradable materials including synthetic [12-14] and natural [15-17] polymers have been exhaustively explored as supportive scaffolds for bone tissue engineering applications. Among them, naturally derived polymers are of special interest due to, as natural components of living structures, their biological and chemical similarities to natural tissues [18].
For surgical implantations, over the last century, biocompatible materials such as metals, ceramics and polymers have been widely used. Ceramics and metal have contributed to major advances in the medical field, mainly in orthopedic tissue replacement. But, metals and ceramics are not biodegradable and their processability is very limited. Therefore, polymer materials have received increasing attention and been extensively used because of easy control over biodegradability and process ability [19-24]. Some of naturally occurring biomaterials and their applications are listed in (Table 1.)
| Type of material | Application | Citations |
|---|---|---|
| Protein based biomaterials | ||
| Collagen | Bone, Cartilage, Heart, Ligament, Nerve, Vasculature | Baharvand et al. (2006); Battista et al. (2005); Chan et al. (2007); Chen et al. (2003); Daya et al. (2007); Gerecht-Nir et al. (2003); Ma et al. (2004); Michelini et al. (2006); Noth et al. (2005); O’Connor et al. (2000); Sumanasinghe et al. (2006); Watanabe et al. (2007) |
| Fibrin | Cartilage, Nerve, Vasculature | Catelas et al. (2006); Gurevich et al. (2002); Im et al. (2005); Liu et al. (2006); Willerth et al. (2006); Willerth et al. (2007); Worster et al. (2001) |
| Silk | Bone, Cartilage, Liver | Altman et al. (2002); Hofmann et al. (2007); Hofmann et al. (2006); Kim et al. (2005); Mauney et al. (2007); Meinel et al. (2005); Meinel et al. (2004a); Meinel et al. (2004b); Meinel et al. (2004c); Wang et al. (2005) |
| Polysaccharide based biomaterials | ||
| Agarose | Cartilage, Heart, Nerve | Ando et al. (2007); Awad et al. (2004); Chen et al. (2007b); Finger et al. (2007); Huang et al. (2004); Mauck et al. (2006); Moriyasu et al. (2006) |
| Alginate | Cartilage, Liver, Nerve, Vasculature | Ashton et al. (2007); Awad et al. (2004); Franzesi et al. (2006); Gerecht-Nir et al. (2004); Hannouche et al. (2007); Jin et al. (2007); Maguire et al. (2006); Prang et al. (2006); Wayne et al. (2005) |
| Hyaluronan | Adipose, Cartilage, Nerve, Skin,Vasculature | Angele et al. (2007); Chen et al. (2007a); Flynn et al. (2007); Flynn et al. (2008); Gerecht et al. (2007); Mehlhorn et al. (2007); Myers et al. (2007) |
| Chitosan | Bone, Cartilage, Nerve, Skin | Cho et al. (2007); Franzesi et al. (2006); Gravel et al. (2006); Mrugala et al. (2007); PP et al. (2005) |
| Polymer based biomaterials | ||
| PLGA | Adipose, Bone, Cartilage, Muscle, Nerve | Bhang et al. (2007); Chastain et al. (2006); Choi et al. (2005), (2007); Graziano et al. (2007); Kim et al. (2003); Kim et al. (2006); Levenberg et al. (2005); Levenberg et al. (2003); Neubauer et al. (2005); Sun et al. (2007); Teng et al. (2002); Tomita et al. (2005); Uematsu et al. (2005); Xin et al. (2007); Yoon et al. (2007) |
| PEG | Adipose, Bone, Cartilage, Liver, Heart, Nerve | Benoit and Anseth, (2005); Benoit et al. (2007); Buxton et al. (2007); Ford et al. (2006); Hwang et al. (2006); Mahoney and Anseth, (2006), (2007); Nuttelman et al. (2004); Royce Hynes et al. (2007); Salinas et al. (2007); Shin et al. (2004); Stosich et al. (2007); Underhill et al. (2007); Varghese et al. (2008) |
| Peptide based biomaterials | ||
| -- | Bone, Nerve | Garreta et al. (2007); Garreta et al. (2006); Gelain et al. (2006); Hamada et al. (2008); Hosseinkhani et al. (2006); Silva et al. (2004) |
| Ceramic based biomaterials | ||
| -- | Bone, Cartilage | Arinzeh et al. (2003); Arinzeh et al. (2005); Bruder et al. (1998); Dennis and Caplan, (1993); Dyson et al. (2007); Gao et al. (2001); Hanada et al. (1997); Kitamura et al. (2004); Kotobuki et al. (2005); Kruyt et al. (2006); Lennon et al. (1995); Marcacci et al. (2007); Meseguer-Olmo et al. (2007); Ohgushi et al. (1996); Shimaoka et al. (2004); Toquet et al. (1999); Turhani et al. (2005); Yamada et al. (2003); Yang et al. (2006) |
Table 1: Distribution of patients according to age group (n=45), (Male=25).
Synthetic polymers
Aliphatic polyesters such as polyglycolic acid (PGA), polylactic acid (PLLA), their copolymers (e.g. PLGA) and polycaprolactone (PCL) are the most commonly used polymers for tissue engineering scaffold applications [26]. While these materials have shown much success as they can be fabricated with a tailored architecture, and their degradation characteristics controlled by varying the polymer itself or the composition of the individual polymer [27-29]. But they have drawbacks including the risk of rejection due to reduced bioactivity. In addition, concerns exist about the degradation process of PLLA and PLGA as they degrade by hydrolysis, producing carbon dioxide and therefore lowering the local pH which can result in cell and tissue necrosis [30]. Hence, recent research includes significant use of naturally occurring polymers in the tissue engineering field.
Structure of chitosan and alginate
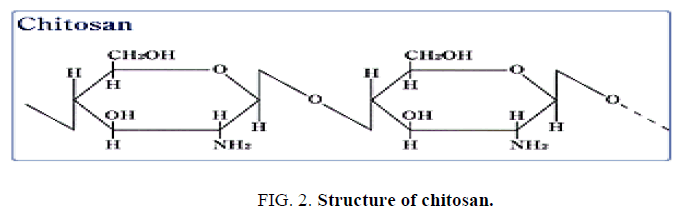
Chitosan is a natural, cationic amino polysaccharide (pKa 6.5) copolymer of glucosamine and N-acetylglucosamine gained by the alkaline, partial deacetylation of chitin. The name chitosan is used for a co-polymer with less than 40 percent DA (i.e., more than 60 percent DD) that, in most cases, will be soluble in dilute acid. Biological source and the extraction procedure used influence the Chitosan quality. Chitosan isolated from crustacean sources like shrimp and crab shells and squid bone plates have a high molecular weight with low polydispersity. (Figure. 2) represents the structure of chitosan.
Pure chitosan is free of antigenic effects, biocompatible, non-toxic, biodegradable and polar. It has been used to prepare a variety of forms like powders, hydrogels, fibers, membranes, beads and porous scaffolds which have been tested in many medical and biological applications. Tissue engineering applications for which chitosan scaffolds have been prepared by the freeze drying and freeze gelation methods and their mechanical and biological properties have been characterized.
The property of Chitosan allows it to rapidly clot blood and gain approval for use in bandages and other hemostatic agents that are used in tests to quickly stop bleeding and reduce blood loss. The chitosan salts can be mixed with other materials to make them more absorbent (such as mixing with alginate), or to vary the rate of solubility and bio-absorbability of the chitosan salt. Chitosan can be used to transport a drug to an acidic environment, where the chitosan packaging will then degrade, releasing the drug to the desired environment. One example has been the transport of insulin.
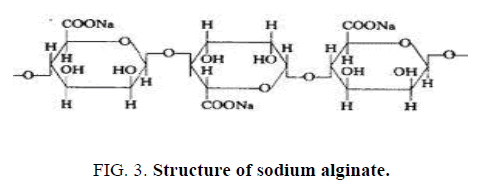
Alginate is usually extracted from seaweed, such as brown algae, or from some bacterial species. They consist of unbranched, binary copolymers of 1-4 linked β-D- mannuronic acid (M) and α-L-guluronic acid (G), of widely varying composition. The structure is influenced by the seaweed source as well as the growing conditions of the weeds. Alginate has carboxyl end groups hence called as an anionic mucoadhesive polymer. (Figure. 3) represents the structure of sodium alginate.
The use of alginate scaffolds in tissue engineering applications is limited, however, owing to their weak mechanical properties, lack of cellular interactions, and uncontrollable degradation. Scaffolds made from alginate are soft and weak, which may limit their further application as templates for tissue regeneration.
Because alginate is hydrophilic, alginate scaffolds have limited protein adsorption capacity; thus, most of cells do not adhere to the scaffold. Furthermore, once the scaffold gets dissolved in the medium, the loss of divalent cations into the surrounding medium causes the ionically cross-linked alginate’s uncontrollable degradation. To improve these limitations, we propose using chitosan as a reinforcing material to make porous alginate-chitosan composite scaffolds.
Chitosan-alginate composites
Chitosan and alginate alone has low mechanical strength and high rates of degradation. Therefore it should be used in composites to improve material properties and reduce degradation rates.
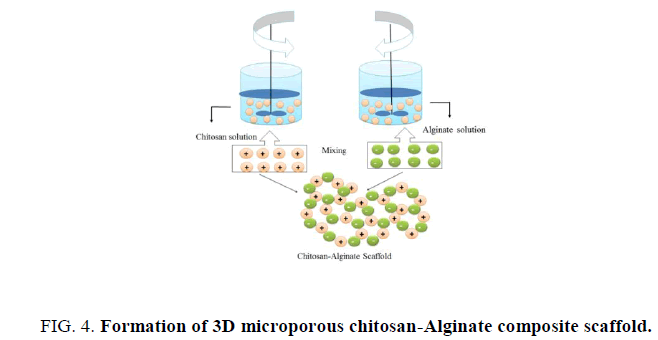
Upon mixing of chitosan and alginate will form a polyion complex. Masuda et al. confirmed that the carboxyl anion of alginate and amino cation of chitosan can form complexes as explain in Figure. 4. These complexes form by mixing in the ratio 8 of 1.1 to 1.2 depends on the specific chitosan and alginate being used which develops a heterogeneous structure produces relatively rough surface on the bulky scaffolds [31-33]. The structural properties and yield is depends on the mixing ratio of these two components. Low concentration chitosan and alginate (<3%w/v) are frequently used for beads or films synthesis for drug release especially growth factors release as the neutral gel forming conditions facilitate these protein based growth factor to be incorporated [34], but we are using high concentrations (>3%w/v) chitosan and alginate for making scaffolds. High concentration hybrid chitosan- alginate scaffold will be discussed more in later chapters.
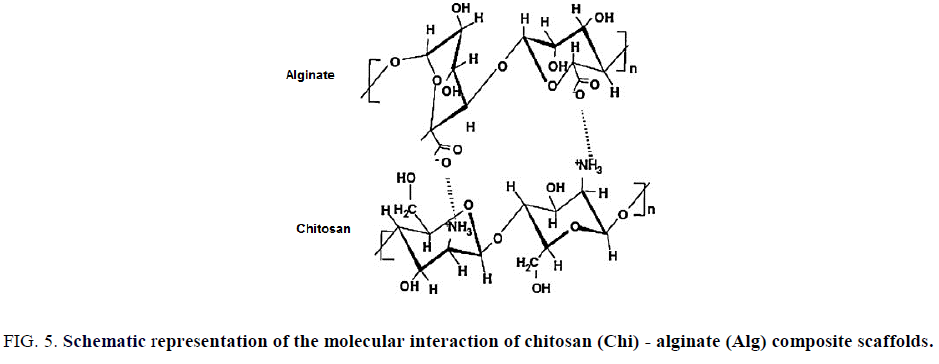
Chitosan-alginate composite do not need certain modifications for better results is its other main characteristic. As both possess opposite charges, interacting with each other forms 3D porous structured scaffolds, they are self-functionalized organic molecules too, hence can get relief from tedious functionalization procedures. Chi-Alg composites have been widely used for drug delivery and protein delivery, wound healing, tendon and ligament tissue engineering and intervertebral tissue engineering (Figure. 5).
Figure 5: Schematic representation of the molecular interaction of chitosan (Chi) - alginate (Alg) composite scaffolds.
Applications of Chitosan-Alginate (CA) Scaffolds
Chitosan
Another polysaccharide that has been explored for tissue engineering applications is chitosan. It is derived by the deacetylation of chitin and consists of glucosamine units. Additionally, the rate of gelation of chitosan scaffolds can be controlled using pH. Chitosan has been used extensively as material for regenerating skin, bone and nerve tissue and has more recently been studied for use in combination with stem cells. One of the studies looked at the ability of such 3D scaffolds to promote osteogenic differentiation of mouse mesenchymal stem cells [35]. This study showed that the addition of corraline, another seaweed derived material, enhanced osteocalcin release over time, which is important for bone formation. A different approach for bone tissue engineering used adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells seeded inside of chitosan particles, which were then aggregated to form scaffolds [36]. Chitosan scaffolds have also been demonstrated to be suitable for mouse ES cell culture as well as for the expansion of stem cells derived from human cord blood [37]. For cartilage tissue engineering, an in vivo study looked at the effects of using chitosan scaffolds seeded with mesenchymal stem cells and transforming growth factor-β as treatment for lesions on the patella of sheep [38]. These cells differentiated into chondrocyte-like cells, demonstrating that such strategies can be effective in vivo. Such studies show that these scaffolds support stem cell differentiation both in vitro and in vivo (Figure. 5).
Alginate
Alginate, which is derived from the cell walls of brown algae, forms scaffolds through the use of ionic cross-linking, allowing for encapsulation of cells. Many studies have evaluated alginate scaffolds as a platform for generating cartilage [39, 40]. Both adipose-derived adult stem cells as well bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells have been shown to survive and differentiate in chondrocytes in these studies. Alginate has also been used for neural tissue engineering applications. One study demonstrated that adult neural progenitor cells seeded inside of alginate scaffolds survived in vivo for two weeks after implantation into a spinal cord injury model [41]. A different study developed tunable alginate scaffolds by incorporating microspheres that released enzymes over time to degrade the scaffold. These scaffolds were successfully used to culture neural progenitor cells and increased their proliferation rate compared to when such cells were cultured in alginate scaffolds without microspheres [42]. Alginate scaffolds have also been used in combination with ES cells to generate hepatocytes and vasculature [43] (Figure. 5).
Chitosan-Alginate (CA) composite Scaffold
CA Scaffolds in growth factor release and drug delivery
In these, the cells with growth factor are encapsulated or seeded in the scaffold and administered into the body. Previously, CA polyelectrolyte complexes in various forms have been used to encapsulate and deliver proteins or drugs by manipulating the degree of association between the two polymers functional groups as well as their pH-dependent charge density [44,45]. For example, CA self-assembling polyelectrolyte multilayer films have been used to immobilize antibodies [45], CA blend gel beads with dual crosslinking were shown to have gastrointestinal site-specific protein release [46], and drug-loaded, polyelectrolyte complexed CA fibers released charged compounds such as bovine serum albumin (BSA), platelet-derived growth factor-bb (PDGF-bb), and avidin over the course of 3 week [47].
Also, three-dimensional scaffolds prepared from the polyelectrolyte complexes (PEC) of chitosan and alginate developed for the delivery of bFGF [48]. Similarly, sponges composed of sodium alginate and chitosan were prepared in order to assess the utility of mixed sponges as potential wound dressings or matrices for tissue engineering application. Such sponges were also used for controlled release of paracitamol [49]. Min Lee et al. [50] showed that CA scaffolds were used as osteogenic protein carriers in the form of microparticles.
CA Scaffolds in tissue engineering
Previous research regarding the use of organic and inorganic materials, including chitosan and sodium alginate, in scaffolds has been conducted. Yet, little research has been documented on the mechanical stability and strength of scaffolds which composed of differing ratios of chitosan and sodium alginate. Many of times chitosan-alginate in the form of scaffolds, beads, hydrogels, and thin films was used for attachment with various cell types and its interaction was studied. Chen et al. [51] carried out analysis of chitosan-alginate bone scaffolds. In this experiment, they examined the scaffolds structural integrity as well as adhesion of cells to it under various conditions. Florczyk et al. [52] used chitosan-alginate scaffold for studying interactions of prostate cancer cells and lymphocyte in vitro. Liz, Zhang, Tigli and Gumusderelioglu [53,54] used chitosan–alginate scaffolds for studying cartilage as well as bone tissue engineering. Similarly, human embryonic stem cells, hepatocytes and annulus fibrosus cells, glioma tumor cells, cultured on chitosan-alginate scaffolds for variety of applications [55-59].
Some modification is also done that enhanced use of chitosan-alginate scaffold as a culture system for many cell types [60]. Used galactosylated chitosan scaffold and alginate for culturing hepatocytes with NIH 3T3 cells which enhanced liver functions of hepatocytes cells. Some combinations with alginate such as polypyrrole –alginate with chitosan used in bone tissue engineering [61]. Yet another combination with hyaluronate was also studied for cartilage regeneration by Ma and Sutradhar et al. [62,63] showed the effect of chitosan-alginate beads with demineralized bone matrix which enhances chondrogenesis. This study demonstrated that chondrocytes co cultured with DBM in chitosan-alginate beads shows enhanced proliferation while keeping the chondrocytic round morphology showing combined superior biological and mechanical properties over its alginate counterpart, raises the possibility of using chitosan-alginate as an improved alternative to alginate for osteochondral repair and regeneration. Leung et al. [64] studied Chitosan- alginate scaffold culture system for hepatocellular carcinoma which increases malignancy and drug resistance.
They have shown the CA scaffold system is a highly reproducible, versatile model of HCC with direct applications for evaluating tumor behavior and the efficacy of novel anticancer therapies. Whu et al. [65], demonstrated evaluation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells seeded into BCII and chitosan-gelatin composite scaffolds and cultured in a dynamic culture system for neocartilage regeneration in vitro. Jose et al. [66] studied Chitosan-collagen scaffolds which can regulate the biological activities of adipose mesenchymal stem cells for tissue engineering. Cruz et al. [67] showed differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in chitosan scaffolds with Double micro and macro porosity. GBMSCs when seeded in Chitosan scaffolds with micro and macropores are able to attach and gradually proliferate along 4 weeks of culture. Sabine Neuss Christian [68] studied assessment of stem cell/biomaterial combinations for stem cell-based tissue engineering. They have used variety of combinations of biomaterials- stem cells, and studied cell adhesion, proliferation, migration, viability properties which can be essential while used as a tissue engineering construct. Pandimadevi et al. [69] demonstrated use of a novel wound dressing material fibrin-chitosan-sodium alginate composite sheet, and applied on the clinical wounds of dogs to find its efficacy as wound dressing material and the study is in progress. Shao and Hunter [70] presented a paper in 52nd Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, entitled Developing an alginate/chitosan hybrid fiber scaffold for intervertebral disc annulus fibrous cells. The study demonstrated the feasibility of alginate-based chitosan hybrid scaffold fabrication and support of annulus fibrosus cell growth. Jeong et al. [71] developed electrospun Chitosan–Alginate Nanofibers with In Situ Polyelectrolyte Complexation for Use as Tissue Engineering Scaffolds. The nanofibrous scaffolds were able to promote the adhesion and proliferation of cells, and they Offer great promise for use a sscaffolds in tissue regeneration strategies. He et al. [72] studied creation and degradation of chitosan-alginate scaffolds for in vitro cell culture. The results show that cells are viable in the chitosan alginate scaffolds and that the cells can be reliably released for study after being cultured in the scaffolds. These scaffolds may be used to support various cell types and can be a great tool in mimicking in vivo conditions in vitro more closely.
Recently, chitosan/gelatin- alginate scaffolds have been used as a tissue engineering construct which can be directly implanted in vivo upon seeding stem cells/proginitor cells. Katesn-Globa et al. [73] and Xuan Meng et al. [74] studied the use of 3D culture systems for stem cell culture and discuss the relationship between stem cells and 3D growth matrices including the roles of the extracellular matrix, scaffolds, soluble factors, cell-cell interactions and shear stress effects within this environment. Francis et al. [75] showed that C/A scaffold is a promising candidate for use as a nerve guidance scaffold, because of its ability to support neuronal attachment and the linearly aligned growth of DRG neuritis. Andersen et al. [76] compiled information regarding the use of alginate, and in particular alginate hydrogels, in culturing cells in 3D. Zhang et al. [77] studied proliferation and differentiation on mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in Alginate-chitosan-alginate microcapsule.
Conclusion
In summary, biomaterial is defined as ‘a nonviable material used into a medical device, which intended to interact with biological systems; given by European Society for Biomaterials (ESB) in 1976, however, the ESB’s current definition is a ‘material intented to interface with biological systems to evaluate, augment, treat or replace any tissue, organ or function of the body. This subtle change in definition is indicative of how the field of biomaterials has evolved. Typically, three individuals groups of biomaterials bioceramics, synthetic polymers as well as natural polymers, are used in the fabrication of scaffold for tissue engineering. Each of this individual biomaterial group has specific advantages and, needless to say, disadvantages so the use of composite scaffolds those comprised of different phases are becoming increasingly common. Use of chitosan-alginate scaffolds in drug delivery and tissue engineering applications is presented by this review. Both chitosan-alginate scaffolds are polysaccharides, naturally occurring, biodegradable and biocompatible organic molecules and it is the main reason to use them. When they combined, they possess desirable mechanical strength and stability. Hence, they can be served as a potential material for tissue engineering applications.
References
- Griffith LG, Swartz MA. Capturing complex 3D tissue physiology invitro. Nat rev mol cell biol. 2006;7:211-24.
- Nehrer S, Breinan HA, Ramappa A, et al. Matrix collagen type and pore size influence behaviour of seeded canine chondrocytes. Biomaterials. 1997;18:769-76.
- DuttaRC, Dutta AK. Cell-interactive 3D-scaffold; advances and applications. Biotechnol Adv. 2009;27:334-9.
- Temenoff JS, Mikos AG. Injectable biodegradable materials for orthopedic tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2405-12.
- Badylak SF. In vivo remodeling. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;961:319-22.
- Griffith LG. Emerging design principles in biomaterials and scaffolds for tissue engineering. Ann NY Acad Sci. 2002;961:83-95.
- Guilak F, Butler DL, Goldstein SA, et al. Biomechanics and mechanobiology in functional tissue engineering. J Biomech. 2014;47:1933-40.
- Karp JM, Dalton PD, Shoichet MS. Scaffolds for tissue engineering. MRS Bulletin. 2003;28:301-6.
- Barbani N, Giusti P, Lazzeri L, et al. Bioartificial materials based on collagen:1. Collagen cross-linking with gaseous gluteraldehyde. J Biomaterscipolym Ed. 2012;7:461-9.
- Sachlos E, Czernuszka JT. Making tissue engineering scaffolds work. Review on the application of solid freeform fabrication technology to the production of tissue engineering scaffolds. Eur cell mater. 2003;5:29-40.
- Preethi GU, Joseph MM, Unnikrishnan BS, et al. Biomedical applications of natural polymer based nanofibrous scaffolds. Int J Med Nano Res. 2015;2:2-9.
- Li M, Mondrinos MJ, Chen X, et al. Co-electrospunpoly(lactide-co-glycolide), gelatin, and elastin blends for tissue engineering scaffolds. J Biomed Mater Res A 2006;79A:963-73.
- Wei G, Ma PX. Structure and properties of nano-hydroxyapatite/polymer composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2004;25:4749-57.
- Lin CY, Kikuchi N, Hollister SJ. A novel method for biomaterial scaffold internal architecture design to match bone elastic properties with desired porosity. J Biomech. 2004;37:623-36.
- Takahashi Y, Yamamoto M, Tabata Y. Osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in biodegradable sponges composed of gelatin and β-tricalcium phosphate. Biomaterials. 200;26:3587-96.
- Li X, Feng Q, Liu X, et al. Collagen-based implants reinforced by chitin fibres in a goat shank bone defect model. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1917-23.
- Shen FH, Zeng Q, Li Q, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stromal cells treated with GDF-5 cultured on a novel three-dimensional sintered microsphere matrix. The Spine journal.2006;6:615-23.
- Krajewska B. Membrane-based processes performed with use of chitin/chitosan materials. Sep Purif Technol. 2005;41:305-12.
- Kim BS, Mooney DJ. Development of biocompatible synthetic extracellular matrices for tissue engineering. Trends Biotechnol. 1998;16:224-30.
- Katz AJ, Llull R, Hedrick MH, et al. Emerging approaches to the tissue engineering of fat. ClinPlast Surg. 1999;26:587-603.
- Karageorgiou V, Kaplan D. Porosity of 3D biomaterial scaffolds and osteogenesis. Biomaterials. 2005;26: 5474-91.
- Kim KS, Baez CE, Atala A. Biomaterials for tissue engineering. World J Urol 2000;8:2-9.
- Kwok KK, Groves MJ, Burgess DJ. Production of 5–15 µm Diameter Alginate-Polylysine Microcapsules by an Air-Atomization Technique. Pharm Res. 1991;8:341-4.
- OldeDamink LHH, Dijkstra PJ, Van Luyn MJA, et al. Glutaraldehyde as a crosslinking agent for collagen-based biomaterials. J Mtaer Sci. 1995;6:460-72.
- Willerth SM, Sakiyama-Elbert SE. Combining stem cells and biomaterial scaffolds for constructing tissues and cell delivery. StemBook org. 2008;1-18.
- Ikada Y. Challenges in tissue engineering. Journal of the royal society interface. 2006;3:589-601.
- Liang D, Hsiao BS, Chu B. Functional electrospunnanofibrous scaffolds for biomedical applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2007;59:1392-412.
- Boland ED, Espy PG, Bowlin GL. In:Encyclopaedia of Biomaterials and biomedical engineering. Wenk G E Bowlin GL. (Edi) 2004;163:1623-35.
- Mandal BB, Kundu SC. Non bioengineered silk gland fibroin protein: Characterization and evaluation of matrices for potential tissue engineering applications. Biotechnology and Bioengineering. 2008;100:1237-50.
- Patel H, Bonde M, Srinivasan G. Biodegradable polymer scaffold for tissue engineering. Trends Biomater. Artif Organs. 2011;25:20-9.
- Desbrieres J. Viscosity of semiflexible chitosan solutions: influence of concentration, temperature, and role of intermolecular interactions. Biomacromolecules. 2002;3:342-9.
- Kjoniksen AL, Nystrom B, Nakken T, et al. Effect of surfactant concentration, pH, and shear rate on the rheological properties of aqueous systems of a hydrophobicallymodifed chitosan and its unmodified analogue. Polym Bull. 1997;38:71-9.
- Matsumoto T, Kawai M, Masuda T. Rheological properties and fractal structure of concentrated polyion complexes of chitosan and alginate. Biorheology. 1993;30:435-41.
- Wang L, Khor E, Lim LY. Chitosan–alginate–CaCl2 system for membrane coat application. J Pharma Sci. 2001;90:1134-42.
- Gravel M, Gross T, Vago R, et al. Responses of mesenchymal stem cell to chitosan–coralline composites microstructured using coralline as gas forming agent. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1899-906.
- Malafaya PB, Pedro AJ, Peterbauer A, et al. Chitosan particles agglomerated scaffolds for cartilage and osteochondral tissue engineering approaches with adipose tissue derived stem cells. J Mater Sci. 2005;16:1077-85.
- Franzesi GT, Ni B, Ling Y, et al. A Controlled-release strategy for the generation of cross-linked hydrogel microstructures. J am chemsoc. 2006;128:15064-5.
- Mrugala D, Bony C, Neves N, et al. Phenotypic and functional characterisation of ovine mesenchymal stem cells: application to a cartilage defect model. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008;67:288-95.
- Awad HA, Wickham MQ, Leddy HA, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of adipose-derived adult stem cells in agarose, alginate, and gelatin scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2004;25:3211-22.
- Hannouche D, Terai H, Fuchs JR, et al. Engineering of implantable cartilaginous structures from bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2007;1387-99.
- Prang P, Muller R, Eljaouhari A, et al. The promotion of oriented axonal regrowth in the injured spinal cord by alginate-based anisotropic capillary hydrogels. Biomaterials. 2006;27:3560-9.
- Ashton RS, Banerjee A, Punyani S, et al. Scaffolds based on degradable alginate hydrogels and poly(lactide-co-glycolide) microspheres for stem cell culture. Biomaterials. 2007;28:5518-25.
- Gerecht-Nir S, Cohen S, Ziskind A, et al. Three-dimensional porous alginate scaffolds provide a conducive environment for generation of well-vascularized embryoid bodies from human embryonic stem cells. BiotechnolBioeng. 2004;88:313-20.
- Yuan W, Dong H, Li CM, et al. Ph-controlled construction of chitosan/alginate multilayer film: Characterization and application for antibody immobilization. Langmuir. 2007;23:13046-52.
- Xu Y, Zhan C, Fan L, et al. Preparation of dual crosslinked alginate–chitosan blend gel beads and in vitro controlled release in oral site-specific drug delivery system. International Journal of Pharmaceuticals. 2007;336:329-37.
- Liao IC, Wan ACA, Yim EKF, et al. Controlled release from fibers of polyelectrolyte complexes. J control release. 2005;104:347-58.
- Ho YC, Mi FL, Sung HW, et al. Heparin-functionalized chitosan–alginate scaffolds for controlled release of growth factor. Int Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2009;376:69-75.
- Lai HL, Khalil AA, Duncan QM, et al. The preparation and characterisation of drug-loaded alginate and chitosan sponges. Int Journal of Pharmaceutics. 2003;251:175-81.
- Lin HR, Yeh YJ. Porous Alginate/HApsponges for bone tissue engineering. Materials Science Forum.2003;26:3043-8.
- Lee M, Li W, Ronald K, et al. Biomimetic apatite-coated alginate/chitosan microparticles as osteogenic protein carriers. Biomaterilas. 2009;30:6094-101.
- Chen A, Haddad D, Wang R. Analysis of chitosan-alginate bone scaffolds. Rutgers University, New Jersey Governor’s School of Engineering & Technology. 2009:1-8.
- Florczyk SJ, Liu G, Kievit FM, et al. 3D Porous chitosan–alginate scaffolds: A new matrix for studying prostate cancer cell–lymphocyte interactions in vitro. Advanced health materials. 2012;5:590-9.
- Li Z, Zhang M. Chitosan-alginate as scaffolding material for cartilage tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2005;75:485-93.
- Tigli RS, Gumusderelioglu M. Evaluation of alginate-chitosan semi IPNs as cartilage scaffolds. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2009;20:699-709.
- Li Z, Leung M, Hopper R, et al. Feeder-free self-renewal of human embryonic stem cells in 3D porous natural polymer scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2010;31:404-12.
- Chung TW, Yang J, Akaike T, et al. Preparation of alginate/galactosylated chitosan scaffold for hepatocyte attachment. Biomaterials. 2002;23:2827-34.
- Shao X, Hunter JC. Developing an alginate/chitosan hybrid fiber scaffold for annulus fibrosus cells. Journal of biomaterials research part A. 2007;82:701-10.
- Seo SJ, Choi YJ, Akaike T, et al. Alginate/galactosylated chitosan/heparin scaffold as a new synthetic extracellular matrix for hepatocytes. Tissue Engineering. 2006;12:33-44.
- Kievit FM, Florczyk SJ, Leung MC, et al. Chitosan–alginate 3D scaffolds as a mimic of the glioma tumor microenvironment. Biomaterials. 2010;22:5903-10.
- Seo SJ, Kim IY, Choi YJ, et al. Enhanced liver functions of hepatocytes co-cultured with NIH 3T3 in the alginate/galactosylated chitosan scaffold. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1487-95.
- Jin HH, Lee C, Lee W, et al. In-situ formation of the hydroxyapatite/chitosan-alginate composite scaffolds. Materials Letters. 2008;62:1630-3.
- Ma PX. Biomimetic materials for tissue engineering. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008;60:184-98.
- Sutradhar BC, Hing G, Ge Z, et al. Coculture of bovine chondrocytes with demineralized bone matrix inchitosanalginate beads enhances chondrogenesis. J Med Boi Eng. 2012;33:518-25.
- Leung M, Kievit FM, Florczyk SJ, et al. Chitosan-alginate scaffold culture system for hepatocellular carcinoma increases malignancy and drug resistance. Pharm Res. 2010;27:1939-48.
- Whu SW, Tsai CL, Hsu S. Evaluation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells seeded into composite scaffoldsand cultured in a dynamic culture system for neocartilage regeneration invitro. Journal of Medical and Biological Engineering. 2009;29:52-8.
- Jose I, Filho Z, Frascino FL, et al. A clinical and radiographic evaluation of the management of periodontal osseous defects with alloplast and platelet rich plasma.Journal of Regenerative Medicine & Tissue Engineering 2013;2(1):12.
- Cruz DM, Gomes M, Reis RL, et al.Differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in chitosan scaffolds with double micro and macroporosity. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2010;95:1182-93.
- Neuss S, Apel C, Buttler P, et al. Assessment of stem cell/biomaterial combinations for stem cell based tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2008;29:302-13.
- Pandimadevi M, Sekar M, Chamundeswari M, et al. A novel wound dressing material –fibrin-chitosan-sodium alginate composite sheet. B mater sci. 2012;35:1157-63.
- Shao XX, Hunter CJ. 52nd Annual Meeting of the Orthopaedic Research Society, Paper No: 1244.
- Jeong SI, Krebs MD, Bonino CA, et al. Electrospunchitosan–alginate nanofibers with in situ polyelectrolyte complexation for use as tissue engineering scaffolds. Tissue Eng Part A. 2011;17:59-70.
- He B, Leung M, Zhang M. Optimizing creation and degradation of chitosan-alginate scaffolds for in vitro cell culture. Journal of Undergradutae Research in Bioengineering. 2010:31-5.
- Katsen-Globa A, Meiser I, Petrenko YA, et al. Towards ready-to-use 3-D scaffolds for regenerative medicine: Adhesion-based cryopreservation of human mesenchymal stem cells attached and spread within alginate–gelatin cryogel scaffold. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2014;25:857-71.
- Meng X, Leslie P, Zhang Y, et al. Stem cells in a three dimensional scaffold environment. Springer Plus. 2014;3:1-8.
- Francis NL, Hunger PM, Donius AE, et al. An ice-templated, linearly aligned chitosan-alginate scaffold for neural tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2013;101A:3493-503.
- Andersen T, Emblem PA, Dornish M. 3D Cell culture in alginate hydrogels. Microarrays. 2015;4:133-61.
- Zhang W, Zhao S, He X. Proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells encapsulated in miniaturized 3D core of alginate-chitosan-alginate (ACA) microcapsules. Arch Stem Cell Res.2015;2:1-6.