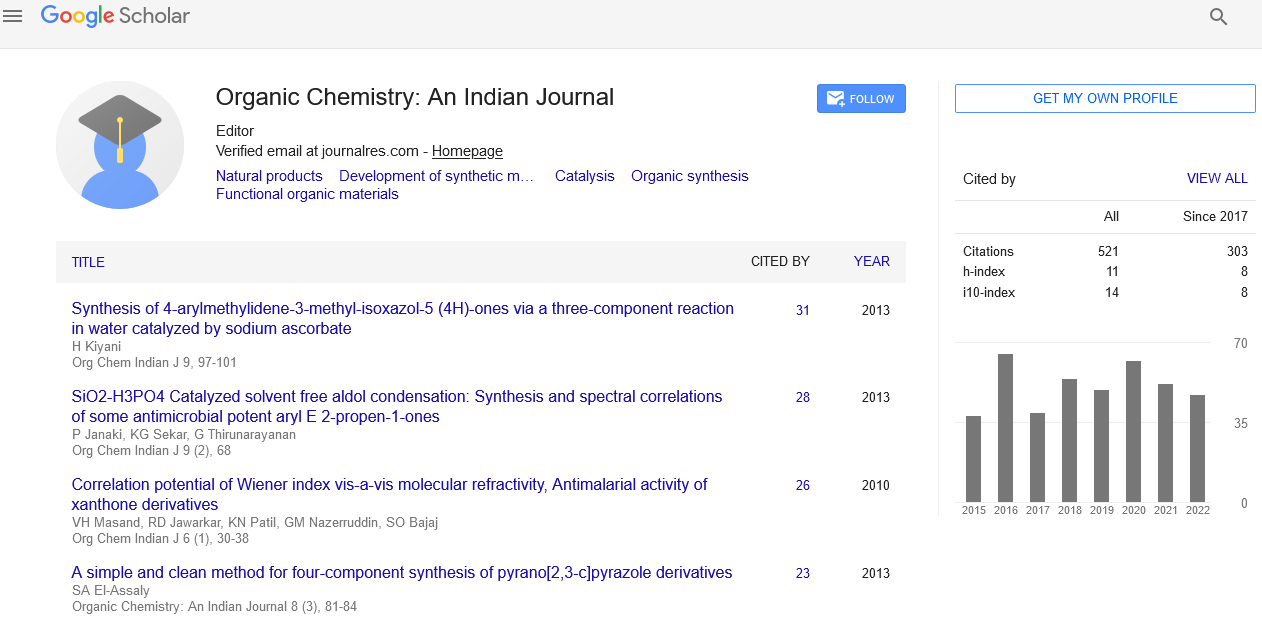
Diffusion
Diffusion is that the process wherein the molecules merge as a results of their K.E. of random motion. It occurs in liquids and gases because their molecules move randomly. The molecules move from a neighbourhood of upper concentration to a neighbourhood of lower concentration, down the concentration gradient, until the concentration equalizes throughout the medium. Types of Diffusion: Since distribution occurs during a sort of conditions, diffusion is often classified into two major types: Simple diffusion and facilitated diffusion. However, there are more sorts of diffusion which are relevant in other disciplines of sciences like atomic diffusion, Knudsen diffusion, kinesis, etc. Simple diffusion: A process during which the substance moves through a membrane with none help from transport proteins. For instance, bacteria deliver small nutrients, water, and oxygen into the cytoplasm through simple diffusion. Facilitated diffusion: Facilitated diffusion may be a passive movement of molecules across the cell wall from the region of upper concentration to the region of lower concentration by means of a carrier molecule.High Impact List of Articles
-
Organoiodine (III) Mediated One-Pot Synthesis of Several New Coumarinyl-Triazolo-Triazines
Pundeer R and Kiran VOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Organoiodine (III) Mediated One-Pot Synthesis of Several New Coumarinyl-Triazolo-Triazines
Pundeer R and Kiran VOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Addition of cyanide to aldehyide and ketons with hetropoly acid praysler.
Hassan hassaniOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Addition of cyanide to aldehyide and ketons with hetropoly acid praysler.
Hassan hassaniOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Microwave induced an efficient synthesis of ¢-enaminones using boric acid as catalyst under solvent-free condition
Balasaheb V.Shitole, S.D.Soluke, Nana V.Shitole, Gopal K.KakdeOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Microwave induced an efficient synthesis of ¢-enaminones using boric acid as catalyst under solvent-free condition
Balasaheb V.Shitole, S.D.Soluke, Nana V.Shitole, Gopal K.KakdeOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
One-pot Mannich type reaction of thiobarbituric acid, aryl aldehyde and aromatic amine in catalyzed by surfactants
Dini Ahanthem, Warjeet S.LaitonjamOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
One-pot Mannich type reaction of thiobarbituric acid, aryl aldehyde and aromatic amine in catalyzed by surfactants
Dini Ahanthem, Warjeet S.LaitonjamOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Tautomerism And Mass Spectra Of Thiomorpholides
Eduardo A.Castro, Patricia E.Allegretti, Facundo Namor, Jorge J.P.FurlongOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
-
Tautomerism And Mass Spectra Of Thiomorpholides
Eduardo A.Castro, Patricia E.Allegretti, Facundo Namor, Jorge J.P.FurlongOriginal Article: Organic Chemistry: An Indian Journal