Inorganic Chemistry: An Indian Journal
ISSN (PRINT):0974-746X
All submissions of the EM system will be redirected to Online Manuscript Submission System. Authors are requested to submit articles directly to Online Manuscript Submission System of respective journal.
Plasmodium Falciparum And HIV-Infections
Plasmodium is a protozoal parasite and a human pathogen. This parasite is the most continuous and generally dispersed reason for repeating intestinal sickness. In spite of the fact that it is less destructive than Plasmodium falciparum, the deadliest of the five human jungle fever parasites, P. vivax jungle fever contaminations can prompt serious malady and passing, regularly because of splenomegaly (a pathologically expanded spleen). P. vivax is conveyed by the female Anopheles mosquito; the guys don't nibble. Plasmodium is found essentially in Asia, Latin America, and in certain pieces of Africa. P. vivax is accepted to have started in Asia, yet most recent examinations have indicated that wild chimpanzees and gorillas all through focal Africa are endemically tainted with parasites that are firmly identified with human P. vivax. These discoveries demonstrate that human P. vivax is of African beginning. Plasmodium vivax represents 65% of jungle fever cases in Asia and South America. Not at all like Plasmodium falciparum, Plasmodium vivax is equipped for experiencing sporogonic advancement in the mosquito at lower temperatures.Google Scholar citation report
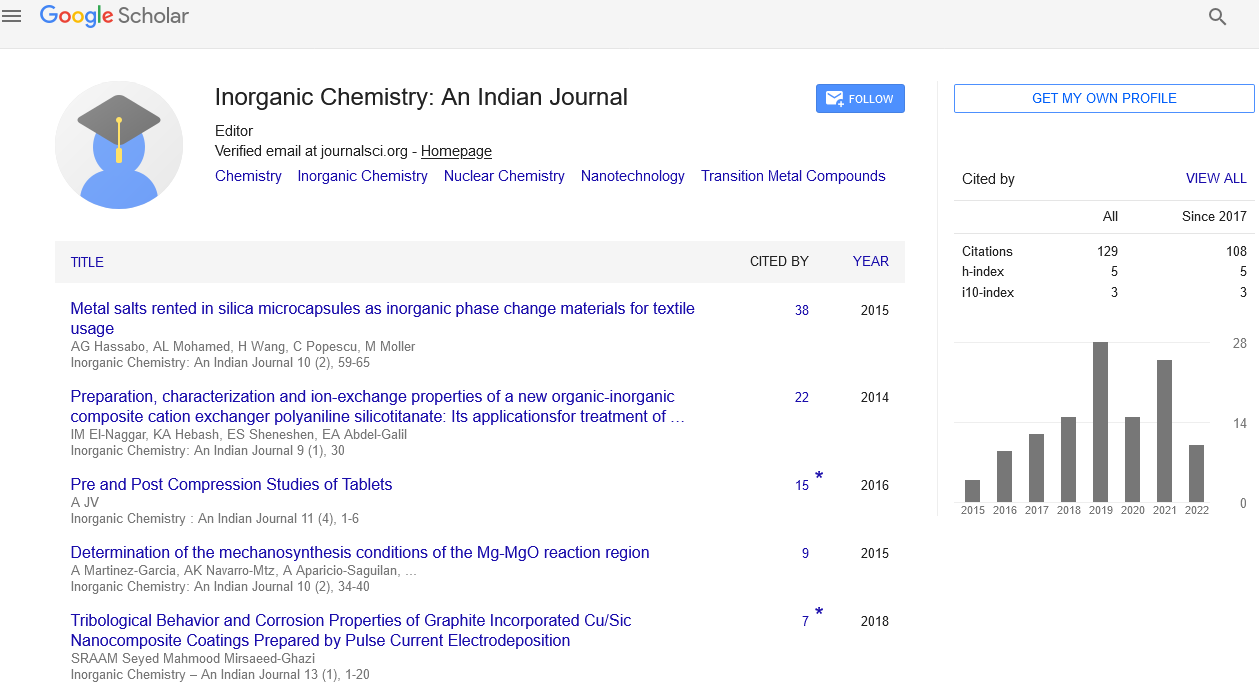
Citations : 160
Inorganic Chemistry: An Indian Journal received 160 citations as per Google Scholar report
Indexed In
- CASS
- Google Scholar
- Open J Gate
- China National Knowledge Infrastructure (CNKI)
- Cosmos IF
- Directory of Research Journal Indexing (DRJI)
- Scholar Article Impact Factor (SAJI))
- Euro Pub
- ICMJE
View More
For Librarians