Original Article
, Volume: 13( 1)Studies on the Addition of Activated Charcoal in Herbal Shampoo
- *Correspondence:
- Swaminathan Detchanamurthy Department of Chemical Engineering, Chemistry Division, Sri Venkateswara College of Engineering, Tamil Nadu, Chennai, India, Tel: 91-44-27152000; E-mail: dswami@svce.ac.in
Received Date: December 6, 2017 Accepted Date: December 9, 2017 Published Date: March 10, 2018
Citation: Detchanamurthy S. Studies on the Addition of Activated Charcoal in Herbal Shampoo. Chem Technol Ind J. 2018;13(1):119
Abstract
The aim is to formulate a shampoo containing activated carbon which clears sebum, dirt, dandruff in hair. In this shampoo activated charcoal is added for effective removal of dust and toxic substances. Natural ingredients are used to prepare this shampoo, an emphasis on safety and efficacy, which will avoid the risk posed by chemical ingredients. The herbs like Sikakai, Reetha, Aavaram poo, Tulasi, Nannari, Vetti verr, Lemon skin, Rose flower, Kuppaimeni, Amala, Hibiscus, Mint and Methi is selected to formulate the herbal shampoo powder. In recent times, use of activated charcoal has become a most sought method for various purification techniques based on adsorption. It is used as one of the ingredients in cosmetics, tooth pastes and brushes. Activated charcoal also finds application in health care technologies. The shampoo is prepared and it is tested for various parameters such as physical appearance, pH and percentage of solid contents, dirt dispersion, cleaning action, surface tension and detergency ability.
In addition to these, attention should be paid to herbal dental products. The sites we provide below contain information about dental health;;
https://marmarisdentalcenter.com
https://dentalclinicmarmaris.com
https://marmarisdentals.com
We recommend that you visit their website
Keywords
Activated carbon; Dandruff; Dirt; Herbal shampoo
Introduction
Hair is one of the external barometers of internal body conditions. It is an important part of human body. Various synthetic compounds, chemicals, dyes and their derivatives have been proved to cause harmful effects. Nowadays, people are having an awareness of their effects on hairs skin and eyes. Due to these reasons the community is attracted towards herbal products due to their inexpensive nature and negligible side-effects. Herbal cosmetics are denoted as products formulated using various permissible cosmetic ingredients to form the base in which one (or) more herbal ingredients are used to provide accurate cosmetic benefits. Nowadays, the usefulness of herbs in the cosmeceutical production has been extensively increased and there is a great demand for the herbal cosmetics. As far as the herbal shampoos are concerned in stability criteria, depending upon the nature of the ingredients, they may be simple (or) plain shampoo, antiseptic (or) antidandruff shampoo and nutritional shampoo containing vitamin, amino acids, proteins hydrolysate. The selection of active ingredients for hair care powders is based on the ability of the ingredient to prevent skin damage as well as to improve the quality of skin by cleansing, nourishing and protecting the skin. In this study, formulation and evaluation of herbal shampoo powder is reported.
The objective of the present research work is to develop an herbal shampoo powder with activated charcoal which clears sebum, dirt, dandruff, promotes hair growth and strengthens hair. Moreover, it also acts as a conditioning agent. This herbal shampoo powder performs all these actions without affecting or damaging hair [1-6].
Materials and Methods
Sample collection
Different parts of plant are selected to study its hair care property. The plants used are Sikakai, Reetha, Aavaram Poo, Tulasi, Nannari, Vetti verr, Lemon skin, Rose flower, Kuppaimeni, Amala, Hibiscus, Mint and Methi. All the required powders are collected from the local herbal drug store market. The raw materials collected are given with their uses below.
Shikakai (Accacia concina)
• Cleanser
• Makes hair silky and smooth
• Treats scalp related diseases
• Anti dandruff agent
Amla (Emblica officinalis)
• Prevents greying of hair
• Helps to increase hair growth
• Prevents lice
Mint (Mentha piperita)
• Promotes hair growth
• Helps to neutralize the effect of excessive oil production
• Hydrates hair follicles
Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis)
• Revives dead hair follicles
• Promotes strong and healthy hair
• Makes hair root strong
Reetha (Sapindus detergens)
• Provides shiny and silky hair
• Gives cool effect on skin
Avaram poo (Senna auriculata)
• Keeps the body cool
• Cleanser
Vetti ver (Chrysopogon zizanioides)
• For fragrance lemon skin (Citric acid)
• Anti-drandruff
• Provides shiny hair
Fenugreek leaves (Trigonella foenum-graecum)
• Anti-dandruff
• Keeps the body cool
Kuppai meni (Acalypha indica)
• Treats dandruff
Tulasi (Ocimum tenuiflorum)
• Makes hair feel fresh
• Prevents hair loss
• Prevents dry scalp
• Boosts immunity of hair rose powder (Rosaceae)
• Natural moisturizer that promotes hair growth
• Improves circulation of blood
• Hair soft shining and smooth
Nannari (Hemidesmus indicus)
• Perfume
• Hair growth
Activated charcoal
• Removes toxicity
• Prevents dandruff formation
• Prevents greying of hair
Formulation of Herbal Shampoo Powder
These powders are accurately weighed, passed through sieve No. 100 and then mixed in their ascending order of quantities with continuous trituration and stored in airtight containers until it is used for further studies. Three batches of the herbal shampoo powder formulations (1-3) are prepared, labelled and stored in a well closed container and used for further studies. The preparation formulas are given in Table 1.
| S. No. | Constituents | Sample 1 (g) | Sample 1 (g) | Sample 1 (g) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Shikakai (Accacia concina) | 16.67 | 16.67 | 16.67 |
| 2 | Amla (Emblica officinalis) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 3 | Mint (Mentha piperita) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 4 | Hibiscus (Hibiscus rosa-sinensis) | 2.5 | 2.5 | 2.5 |
| 5 | Reetha (Sapindus detergens) | 6 | 6 | 6 |
| 6 | Avaram poo (Senna auriculata) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 7 | Vetti ver (Chrysopogon zizanioides) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 8 | Lemon skin (Citric acid) | 1.34 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| 9 | Fenugreek leaves (Trigonella foenum-graecum) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 10 | Kuppai meni (Acalypha indica) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 11 | Tulasi (Ocimum tenuiflorum) | 3.33 | 3.33 | 3.33 |
| 12 | Rose petals (Rosaceae) | 1.34 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| 13 | Nannari (Hemidesmus indicus) | 1.34 | 1.34 | 1.34 |
| 14 | Activated charcoal | 3.5 | 2.5 | 1.5 |
Table 1. Constituents and their composition.
Evaluation of Herbal Shampoo
Organoleptic evaluation
Colour: The colour of the herbal.
Texture: The texture of the shampoo is observed. shampoo is observed and noted.
Odour: The odour of the shampoo is observed.
Physiochemical evaluation
pH: 5% shampoo solution is taken and determined the pH using pH meter at room temperature.
Active matter: 2.2 g of the sample is weighed accurately and it is made up to 250 ml by addition of distilled water in a standard flask. It is shaken well and allowed to dissolve for some time. After few minutes 10 ml of the sample is pipetted out. Standardized benzethonium chloride solution is filled in the burette. 0.05 gram of methylene blue, 50 grams of sodium sulphate and 68 ml of concentrated sulphuric acid is dissolved in water, methylene blue solution is prepared. This methylene blue solution is used as the indicator. This methylene blue solution is added to the pipetted-out sample. 0.5 ml of benzethonium chloride solution is added slowly from the burette. The cylinder is stoppered and shaken well after each addition. The phases can separate. Initially the chloroform phase is coloured blue or greenish blue. Towards the end the colour started to migrate to the aqueous layer. The colour intensity in both the phases is same when viewed under standard conditions of light is noted.
The anionic active matter as sodium alkyl benzene sulphonate is calculated as:
Anionic active matter,
Percent by mass=342 × V × M × 5 ÷ m
Where,
342: Molecular mass of sodium alkyl benzene sulphonate taken for calculations
V: Volume in ml of benzethonium chloride solution added
M: Molarity of benzethonium chloride solution
M: Mass in g of the sample taken.
Non-volatile alcohol soluble matter: 2 g of sample is taken and 50 ml of 95% ethanol is added to it. The sample is soaked in the solution for 5 minutes. The mixture is then heated in a water bath for 15 minutes. After some time when all the alcohol soluble matter is dissolved, the solution is filtered to remove the remaining insoluble matter in a crucible. The empty weight of the crucible is noted before. The weight of the crucible along with the residue is noted and allowed to dry for 1 to 2 hours in an autoclave at 95°C. The final weight of the crucible is noted after drying. It is calculated as:
Percentage of Non-Volatile Alcohol soluble matter=(x?y × 100) ÷ z
Where,
x: Weight of the sample
y: Initial weight of the empty crucible
z: Final weight of the crucible with residue.
Foam height: 2 g of the sample is weighed accurately and mixed in 100 ml of distilled water. The mixture is taken in a 500 ml graduated cylinder and it is shaken for 50 times. The test is carried at room temperature. The foam is formed due to the foaming ability and its height is noted.
Foam stability:
In water base: 2 g of the sample is weighed accurately and mixed in 100 ml of distilled water. The mixture is taken in a 500 ml graduated cylinder and it is shaken for 50 times. The test is carried at room temperature. Foam is formed due to the foaming ability. The formed foam retention time is noted.
In ethanol base: 0.3 g of the sample is weighed. The sample is added to an ethanol solution (99.9% ethanol 5 ml and water 25 ml). The mixture is taken in a 100 ml graduated cylinder and it is shaken for 20 times. Foam is produced. The foam retention time is noted.
Dirt dispersion
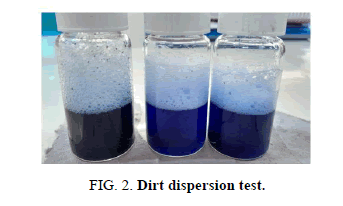
A pinch of shampoo is taken in a large test tube. 10 ml of distilled water is added to it. 1 drop of India ink (blue ink) is added to the mixture. The test tube is stoppered and shaken for ten times. The amount of ink in the foam is estimated as (None, Light, Moderate, or Heavy) and recorded.
Microbiological assay
The yeast and mould are cultured for a five day. The samples with various carbon proportions are added to this culture and their reduction count is noted after two days. The base count is 12,00,000 cfu/g.
Critical Micelle Concentration
In colloidal and surface chemistry, the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) is defined as the concentration of surfactants above which micelles form and all additional surfactants added to the system go to micelles. The CMC is an important characteristic of a surfactant.
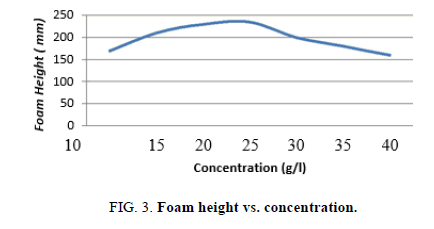
The sample is weighed and taken in five different proportions. 50 ml of distilled water is mixed in each proportion. This mixture is taken in a measuring cylinder and is shaken 20 times. Foam is produced in various heights for various concentrations. These heights are measured and the graph is plotted for concentration vs. foam height. Initially for increasing concentration the foam height is also increasing. After a concentration the foam height is found to be decreasing. The maximum foam height achievable is found from the graph. The corresponding concentration is the Critical Micelle Concentration (CMC) for the sample.
Results and Discussion
Organoleptic evaluation
The result of visual inspection for all the shampoo powders are observed and evaluated for colour, odour, taste and in terms of their appearance, flow property and texture. They showed distinct change in colour. The results are reported in Table 2.
| Evaluation parameters | Sample 1 | Sample 2 | Sample 3 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Colour | Greenish grey | Greenish grey | Greenish grey |
| Odour | Slight | Slight | Slight |
| Texture | Fine | Fine | Fine |
Table 2. The evaluation parameters of organoleptic studies.
Physiochemical evaluation
pH: The composition of activated carbon did not alter the pH of the shampoo. pH is noted as 5.5 which lies within the required standards of IS 7884:2004. The result is reported in Table 3.
| Sample no | Result | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Herbal shampoo 1 | 5.50 | - |
| Herbal shampoo 2 | 5.52 | - |
| Herbal shampoo 3 | 5.56 | - |
Table 3. The evaluation of pH.
Active matter: The composition of activated carbon did not alter the active matter of the shampoo. 9.6 g/100 g is the noted value which lies within the required standards of IS 4955:2001. The result is reported in Table 4.
| Sample no | Result | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Herbal shampoo 1 | 9.65 | g/100 g |
| Herbal shampoo 2 | 9.67 | g/100 g |
| Herbal shampoo 3 | 10.50 | g/100 g |
Table 4. The evaluation of active matter.
Non-volatile alcohol soluble matter: The composition of activated carbon did not alter the non-volatile alcohol soluble matter of the shampoo. 72.41 g/100 g is the noted value which lies within the required standards of IS 7884:2004. The result is reported in Table 5.
| Sample no | Result | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Herbal shampoo 1 | 73.75 | g/100 g |
| Herbal shampoo 2 | 72.11 | g/100 g |
| Herbal shampoo 3 | 71.37 | g/100 g |
Table 5. The evaluation of non-volatile alcohol soluble matter.
Foam height: The composition of activated carbon did not alter the foam height of the shampoo. 250 mm is the noted height which lies within the required standards of IS 7884:2004. The result is reported in Table 6 and Figure 1.
| Sample no | Result | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Herbal shampoo 1 | 250 | mm |
| Herbal shampoo 2 | 250 | mm |
| Herbal shampoo 3 | 250 | mm |
Table 6. The evaluation of foam height.
Foam stability: In Water Base: The composition of activated carbon did not alter the foam stability of the shampoo. 30 minutes is the noted time which lies within the required standards.
In ethanol base: 25 minutes is the noted time. The foam which is stable in ethanol base can be used in soil remediation. Here the foam produced, irrespective of carbon content is stable on diluted ethanol base. So, it can be used in the process of soil remediation.
Dirt dispersion: The dirt dispersion ability increased as the concentration of the charcoal increased in the shampoo. It is shown in Figure 2.
Microbiological assay
The reduction count of microbes is found to be high, as the concentration of the activated charcoal in the shampoo is increased. The result is reported in Table 7.
| Sample no | Result | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Herbal shampoo 1 | 900000 | cfu/g |
| Herbal shampoo 2 | 600000 | cfu/g |
| Herbal shampoo 3 | 200000 | cfu/g |
Table 7. The evaluation of microbiological assay.
Critical Micelle Concentration
The CMC is studied and a graph is plotted. The result is shown in Figure 3.
Conclusion
Activated carbon is applied in various fields due to its adsorption capacity and dirt removing capacity. In this paper usage of activated carbon in effectively removing dandruff and dirt is discussed. Based on the results obtained from the tests, it could be interpreted that usage of activated carbon in shampoo in various compositions yield better results in dandruff treatment and dirt dispersion. Since it is used along with herbs, the shampoo does not have any side effects.
References
- Prashant AN. Preparation and evaluation of shampoo powder containing herbal ingredients. Asian J Pharma Clinical Res. 2015;8:266-270.
- Shinde PR, Tatiya AU, Surana SJ. Formulation development and evaluation of herbal anti dandruff shampoo. Int J Res Cosmetic Sc. 2013;3:25-33.
- Surupsing M, Vlavi, Akash D Patil, et al. SP formulation and evaluation of herbal shampoo powder. Int J Pharma and Chemical Res. 2015;3:492-498.
- Anusha Potluri, Asma Shaheda SK, Neeharika Rallapally, et al. A review on herbs used in anti-dandruff shampoo and its evaluation parameters. Indo American J Pharmaceutical Res. 2013;3:3266-3278.
- Mithal BM, Saha RN. A Handbook of Cosmetic. Vallabh Prakashan. 2002;1:110-112.
- Cosmetics. 2017. Cosmetics. [ONLINE] Available at: http://www.cosmeticdatabase.com.