Short communication
, Volume: 7( 1) DOI: 10.37532/2320-6756.2019.7(1).171Constant-Roll F(R) Gravity Inflation Solution
- *Correspondence:
- Hebzibha Isravel Aeronautical Department, Sha-Shib College of Engineering, Bangalore, Karnataka 562104, India, E-Mail: hebzi.hebzi@gmail.com
Received: November 10, 2018; Accepted: December 27, 2018; Published: January 05, 2019
Citation: Hebzibha Isravel. Constant-Roll F(R) Gravity Inflation Solution. J Phys Astron. 2019;7(1):171.
Abstract
In this letter, the issue of flatness in the standard Big Bang model is approached with the different perspective where the inflation theory is framed with the constant-roll model of modified gravity F(R) by addressing the reheating phenomena.
Keywords
Inflation; Flatness problem; Modified F(R) gravity; Constant roll approximation
Introduction
So far the visible universe which we observe in our night sky has been explained overall with its key features by the standard concept of Big Bang Cosmology on a cosmic scale. The model further showed consistency with the observed data of Cosmic Microwave Background (CMB) and Large Scale Structure (LSS) involving the nuclear as well as plasma physics of the formation of the early universe to some extent [1]. But the model has faced various shortcomings when it is observed on different levels which provoked the emergence of inflationary theory to provide necessary explanations. It is suggested that the initial conditions of the large-scale structure of the universe such as galaxies can be explained by Inflationary theory. This theory is built on the basis of the expansion of the scale factor in a very minuscule time span exponentially in the early universe in an epoch [2]. Few complications in the standard model include the horizon, flatness and monopole problem. Solving these issues required models with scalar fields either by single [3] or manifold [4] and several models of inflation with the modified gravity in its various forms [5]. F(R) modified gravity theory is one such theory renders a simple theoretical framework which also proved to be compatible with the recent observations of Planck Data [6]. So, in this letter, a quick opinion of approaching one of the inconsistencies of the standard model namely, Flatness problem, with the inflation theory by incorporating F(R) framework is suggested.
Let us assume the cosmological model to be Friedmann-Robertson-Walker metric (FRW) in the polar coordinates as
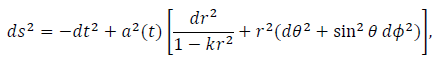 (1)
(1)
where t is time a(t) is the cosmic scale factor of the universe and k is the constant representing the spatial curvature. One of the equations which govern the function a(t) is
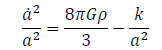 (2)
(2)
where Hubble parameter 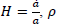 is the density of the universe and G is the gravitational constant related to Planck’s mass
is the density of the universe and G is the gravitational constant related to Planck’s mass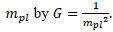 From the Eq. (2), the density parameter
From the Eq. (2), the density parameter 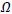 can be obtained as
can be obtained as
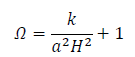 (3)
(3)
Where 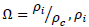 is the density of the various components inhabiting the universe and
is the density of the various components inhabiting the universe and 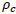 is the critical density. Types of the universe depend upon the conditions of density parameter
is the critical density. Types of the universe depend upon the conditions of density parameter 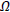 and k as
and k as
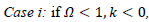 then it is an open universe.
then it is an open universe.
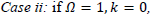 then it is a flat universe.
then it is a flat universe.
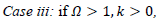 then it is a closed universe.
then it is a closed universe.
The standard model suggests the condition of the case (ii) (flatness) imparting the instability in the shape of the universe hence a minor commotion of the magnitude 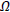 can instigate the curvature in the geometry. Further, the entity 1/aH is the function of t at different early epochs of the Inflationary era:
can instigate the curvature in the geometry. Further, the entity 1/aH is the function of t at different early epochs of the Inflationary era:
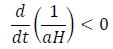 (4)
(4)
Hence we can manipulate the 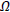 value at by incorporating time and it is recommended that the observed values prefer
value at by incorporating time and it is recommended that the observed values prefer 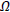 -1 to be nearly zero. This problem can be solved by the perfect fluid cosmological model with the inclusion of the term cosmological constant
-1 to be nearly zero. This problem can be solved by the perfect fluid cosmological model with the inclusion of the term cosmological constant 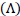 where the equation of state is
where the equation of state is 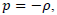 where
where 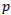 is the pressure. At the inflation zone, the scale factor indicates the exponential expansion of the universe retaining the constant H parameter is as follows:
is the pressure. At the inflation zone, the scale factor indicates the exponential expansion of the universe retaining the constant H parameter is as follows:
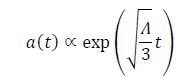 (5)
(5)
Thus this commences the inflation by satisfying the condition in Eq. 4 at the early phase named as de sitter stage. However, the inclusion of 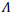 sets up a further consequence of the reheating process. A reheating era emerges once the inflationary era ends and thus proceeds with the radiation and matter dominating epochs. When the de sitter period is reached, due to its rapid expansion, it will be cold and at when the necessity of the thermalization arises for the matter in the universe [7]. The modified gravity theory of
sets up a further consequence of the reheating process. A reheating era emerges once the inflationary era ends and thus proceeds with the radiation and matter dominating epochs. When the de sitter period is reached, due to its rapid expansion, it will be cold and at when the necessity of the thermalization arises for the matter in the universe [7]. The modified gravity theory of 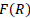 can be used to stimulate the reheating activity immediately at the exit of inflation [8].
can be used to stimulate the reheating activity immediately at the exit of inflation [8].
The Essential feature includes the gravitational action of the 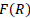 .
.
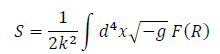 (6)
(6)
Where g is the trace of the background metric.
Constant-roll inflation model
The recent promising analysis of reheating using the F(R) gravity is with the constant-roll approximation. The interesting property of the model is the non-Gaussianities predictions, so the Non- Gaussianities in the power spectrum of the primordial curvature perturbations can be studied precipitately in the future [9]. The assumption for the constant-roll is expressed as [10]
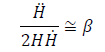 (7)
(7)
Where β is a real parameter. Holding the above condition true for the gravitational equation of motion obtained by the variation of action (Eq. 6) with the metric tensor in the case of R2 model [11], we get
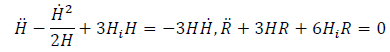 (8)
(8)
Where R is the Ricci Scalar and Hi is a phenomenological parameter of unit mass2. Substituting the Eq. (7) in the first equation of Eq. (8) and by solving the differential equation, we get
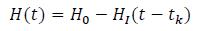 (9)
(9)
where Ht is the function of Hi and β.
Now, Let the time th be the time at which the reheating process begins, Hubble rate can be obtained for 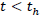 as in equ. (9) and for
as in equ. (9) and for 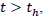 it is yielded by the first part of the Eq. (9) as
it is yielded by the first part of the Eq. (9) as
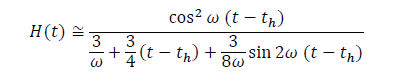 (10)
(10)
Where 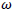 can be obtained from the condition
can be obtained from the condition 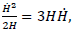 combined with the Eq. (9) and (10), we yield
combined with the Eq. (9) and (10), we yield
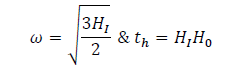 (11)
(11)
The scale factor at the reheating era is given as
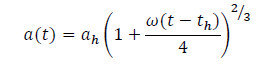 (12)
(12)
Where 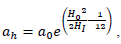 a0 is the initial scale factor at the commencement of inflation.
a0 is the initial scale factor at the commencement of inflation.
In summary, from the Eq. (10) , we can deduce that the Hubble rate increases with the time, proving that the reheating progress with the evolution of the time indicating the early time acceleration of the time and also the scale factor, on the other hand, expands abruptly which can be easily inferred from the Eq. (12). The term R2has combined the inflation with the dark energy [12]. Also, the minimal curvature specifies the possible correlation with the physical observations of the universe.
References
- Tegmark M, Zaldarriaga M, Hamilton Andrew JS. Towards a refined cosmic concordance model: joint 11-parameter constraints from CMB and large-scale structure. Physical Review Zaldarriaga. 2001;63:043007.
- DodelsonS. Modern cosmology, Academic Press, Amsterdam, Netherlands. 2003:440.
- Vazquez JA, Luis, Padilla E, et al. Inflationary cosmology: From Theory to Observations. 2018:1-37.
- Byrnes CT, Choi KY. Review of local non-Gaussianity from multi-field inflation. Advanced Astronomy. 2010:724525.
- Bamba K, Odintsov SD. Inflationary cosmology in modified gravity theories. Symmetry. 2015;7:220-40.
- Odintsov SD, Oikonomou VK. Reconstruction of slow-roll gravity inflation from the observational indices. Annals of Physics. 2018;388:267-75.
- Amin MA, Hertzberg MP, Kaiser DI, et al. Nonperturbative dynamics of reheating after inflation: A review. International Journal of Modern Physics. 2015;24:1530003.
- Mijic MB, Morris MS, Suen WM. The R2 cosmology: Inflation without a phase transition. Physics Review. 1986;34:2934.
- Oikonomou VK. Reheating in constant-roll F(R) gravity. 2017;32: 1750172.
- Nojiri S, Odintsov SD, Oikonomou VK. Constant-roll inflation in F(R) gravity. 2017;341-17.
- Starobinsky AA. Physics letter B.1980;91:99-102.
- Bamba k, Nojiri S, Odintsov SD. Future of the universe in modified gravitational theories: Approaching to the finite-time future singularity. JCAP. 2008;0810:045.